Detailed trials assessing a broad range of regenerative farming strategies on a progressive Durham farm are putting some solid science into efforts to improve arable sustainability by making the very most of above and below-ground biology.
Now into their third season, the Agrii Green Horizons trials with David Hankey on his family’s 160ha Dunkirk Farm, Birtley overlooking Gateshead’s Angel of the North are examining the impact of a wide variety of cover and OSR companion cropping approaches as well as in-field wildlife strips. Indepth assessments are being made of just about everything that can be measured to assess both their specific contributions and, more importantly, the benefits they bring to overall farm sustainability.

To address a serious deterioration in the health and condition of the sandy loam soils which became starkly apparent in the wet winter of 2012, David made the decision to ‘go regenerative’ the following year. Since then he has done away with cultivations, broadened his rotation, developed his own cover and companion cropping regimes and givenup using insecticides entirely. At the same time, he has been routinely applying around 25t/ha of compost and other manures to approximately half the acreage each year, more than replacing the value of the cereal straw – all of which is baled for the very valuable local market.

As well as dramatically reducing problems of surface erosion on the farm’s exposed and sloping ground, this approach has transformed soil health and workability, boosted organic matter levels to 5-6%, lifted worm counts to as many as 30 per spadeful, and generated a wonderful surface tilth to aid crop establishment. This has resulted in impressive 7.5t/ ha-plus light land spring malting barley yields from little more than 120 kg/ha of nitrogen and oilseed rape doing 4t/ ha from just 106 kg/ha, together with reductions around 80% in establishment diesel use.
“Taking the regenerative route has paid dividends from Day One,” says Mr Hankey. “Our soils have become that much easier to work. They don’t slump anymore and we seldom see water on the surface for more than a day. Putting life back into our soils has worked wonders for natural predators too. When we see aphids in our beans we no longer panic. Within a few days they’re being decimated by ladybirds.

“We went into strip tillage with a contractor but invested in our own Claydon in 2015. It didn’t take us long either to replace proprietary cover crop mixes with our own designs – the best of which we’ve christened Jeremy (Clarkson) for its combination of speed and power. “Having tried a variety of no-till disc drills, we’ve finally settled on a Horsch Avatar multi-hopper model to give us greater flexibility to further develop our ‘whole food web’ regenerative ideas,” he says. “The science Agrii and its partners are bringing to our efforts means we’re able to do this with a very much better understanding of what’s going on ecologically.”
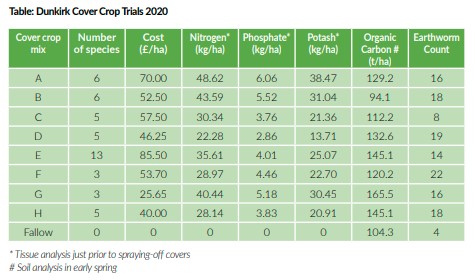
In the past year the Agrii team led by local specialist, Rob Bowes have been examining no less than eight cover crop mixes of three to 13 different species on a field scale after winter wheat and ahead of spring barley. Costing from £26 to £86/ha, these have resulted in very different levels of soil nitrogen, phosphate and potash as well as overall organic carbon, active carbon (available for soil microbes), total microbial biomass and earthworm counts.
“The more diverse mixes have generally delivered greater nutrient and biological benefits,” Mr Bowes reports. “While they have also tended to be more costly, this certainly hasn’t always been the case. Two of our three-species mixes, for instance, varied in cost from £26 to £54/ha, with the cheapest one making a noticeably greater contribution to the main soil nutrients and organic carbon (Table).
“Important in managing residues, fertiliser regimes and nutrient cycling, the mixes have also had very different carbon:nitrogen ratios,” he adds. “In general, the bigger the above and below ground biomass, the higher the carbon content, the slower the cover will release its nutrients and the more nitrogen it will use to do so. “We reckon a C:N ratio of around 30:1 offers the best balance between reasonably rapid residue breakdown and soil surface protection in most cases. Having said that, the best ratio for any particular situation will depend on the relative importance of the two priorities.”
Like catch crops ahead of winter cereals, rapid residue breakdown that ties-up as little N as possible is likely to be preferrable in oilseed rape companion crops, favouring lower C:N ratio species like legumes.

This, and Dunkirk Farm’s experience to date, is why the parallel companion cropping trials have primarily involved mixtures of buckwheat with vetch and berseem clover – plus phacelia and fenugreek to explore if these add anything in crop growth, nutrient contribution, soil structuring or CSFB confusion.
“As well as concealing the OSR from migrating adult flea beetles, our work confirms buckwheat is making a particular contribution to soil phosphate,” notes Mr Bowes. “We also believe its early flowering is helping support the wasps that parasitise both flea beetle adults and larvae.
“We’re finding the vetch that takes over as the dominant companion after the buckwheat dies back valuable in maintaining crop cover for pigeon deterrence, while the berseem clover is giving us great soil structuring. And, of course, both are contributing extra nitrogen in the spring and early summer.

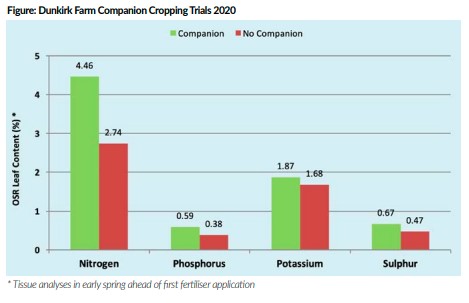
“Our comprehensive soil and tissue testing indicates the companions are delivering around 50kg N/ha to the crop. At the same time, we have recorded noticeably higher levels of phosphorus, potassium and sulphur, as well as boron and molybdenum in OSR leaf tissue testing from our companion cropped areas (Figure); levels which were particularly elevated where we had a more diverse companion mix and replaced seedbed DAP with a specialist protected phosphate Agrii-Start fertiliser.”
The visible differences in both crop health and grass weed control recorded in the Agrii trials at Dunkirk Farm have been especially impressive too. What’s more, adult flea beetle damage has been negligible in either of the two trial fields despite serious levels of grazing in the brassica component of adjacent cover crops. Which offers another valuable lesson in integrated farm-wide pest management. The covers in the nearby field, sown a couple of weeks later than OSR and its companions on August 12, emerged into the peak of CSFB migration and clearly acted as a useful trap crop.
“This sequence of sowing is an inevitable consequence of our rape going in after winter barley and covers following winter wheat ahead of spring barley in our six-year rotation,” Mr Hankey observes. “So, as the beetles arrive in September, we have reasonably well-established oilseed rape nicely sheltered by buckwheat on the one hand and fresh brassicas just coming through in neighbouring covers on the other.
“The scientists tell us flea beetles have a marked preference for younger plants, and this is crystal clear from the fact that our OSR volunteers are seldom touched. Getting companion and cover crops to work together in this way gives us what is basically a ‘pop-up rainforest’ harvesting sunlight and carbon while really make trap-cropping work.”
Another element of wider IPM looking very positive in current Dunkirk Farm trialling is wildlife strips within crops to provide readily available food and cover for predators. Three metre strips of bee and pollen and nectar mixes have so far been sown into the centre of two fields of spring barley, with an average of 25 carabid beetles/trap collected in each of their three pitfall traps last summer.
“That’s a healthy population for beetles the experts tell us we should only be finding within a few metres of our field margins,” points out Mr Hankey. “What’s more, we think they’re going for slug eggs – carabid caviar perhaps? We’re certainly not having to use nearly as many slug pellets these days.”
“There’s a lot more our trial work here and on farms across the country is looking to understand about these and other aspects of biological crop management,” concludes Mr Bowes. “As well as the best place to use covers and companions and the best species to include for particular circumstances, we need more intelligence on when and how best to establish and remove them; especially with soil types, at elevations and in other situations where farming conditions are more challenging than most.